libdbus上手教程
网站:https://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/dbus/ 代码:https://github.com/freedesktop/dbus
What is D-Bus?
D-Bus is a message bus system, a simple way for applications to talk to one another. In addition to interprocess communication, D-Bus helps coordinate process lifecycle; it makes it simple and reliable to code a "single instance" application or daemon, and to launch applications and daemons on demand when their services are needed.
概括:
- 一个消息总线系统
- 一对多(signal):类似于广播/订阅,可以携带消息数据,没有应答确认
- 一对一(method call):有应答确认
- 其他功能
- 启动其它进程
- 支持单个实例进程
- 在 app 退出的时候,通知程序
系统 bus 和会话 bus
system bus:在引导时就会启动,应用场景(待定) session bus:在用户登录后启动,属于那个用户私有。它是用户的应用程序用来通信的一个会话总线。
Low-level API vs high-level binding APIs
low-level API:libdbus high-level binding APIs:GLib, Qt, Python, Mono, Java, or whatever.
区别:
- low-level:依赖少,用起来更加麻烦/复杂,定制程度可以更高,更加适合自己封装,改造
- high-level:用起来更加方便
Version numbers
软件版本格式:major.minor.patch
minor version 是偶数的是 stable 版本,奇数的是 dev 版本 比如, development snapshots: 1.1.1, 1.1.2, 1.1.3, 1.3.4. Stable versions: 1.0, 1.0.1, 1.0.2, 1.2.1, 1.2.3
D-Bus 中的概念
通过一个一对一通信流程来解释:
- 启动 bus daemon, 生成 bus address(unix:path=/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket)
- 获取 bus daemon 的 connect 连接, 注册 bus name(com.mycompany.TextEditor)
- 创建 msg, 发给哪个 bus name(进程)->obj(实例)->Interface->Method
- 发送 msg 到 bus daemon
- bus daemon 发送到相应的 bus name 进程
- 接收到消息后返回数据
- ...
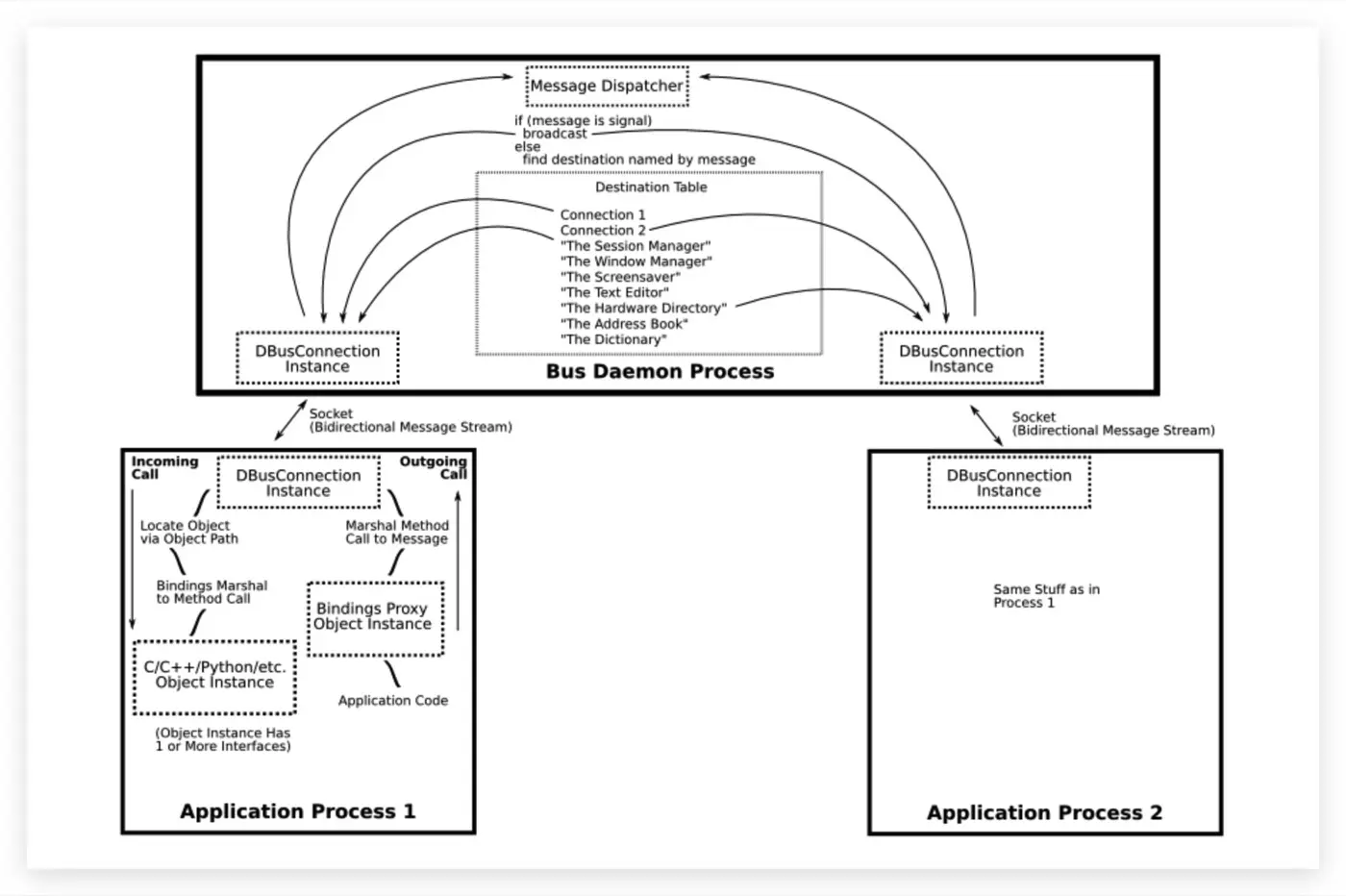 相应概念:
相应概念:
Address(bus) –> Bus Name(进程) –> Object path(实例) –> Interface –> Method
| A... | is identified by a(n)... | which looks like... | and is chosen by... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bus | address | unix:path=/var/run/dbus/system_bus_socket | system configuration |
| Connection | bus name | :34-907 (unique) or com.mycompany.TextEditor (well-known) | D-Bus (unique) or the owning program (well-known) |
| Object | path | /com/mycompany/TextFileManager | the owning program |
| Interface | interface name | org.freedesktop.Hal.Manager | the owning program |
| Member | member name | ListNames | the owning program |
D-Bus FAQ 4. What is the difference between a bus name, and object path, and an interface?
If you imagine a C++ program that implements a network service, then the bus name is the hostname of the computer running this C++ program, the object path is a C++ object instance pointer, and an interface is a C++ class (a pure virtual or abstract class, to be exact). In Java terms, the object path is an object reference, and an interface is a Java interface. People get confused because if they write an application with a single object instance and a single interface, then the bus name, object path, and interface look redundant. For example, you might have a text editor that uses the bus name org.freedesktop.TextEditor, has a global singleton object called /org/freedesktop/TextEditor, and that singleton object could implement the interface org.freedesktop.TextEditor. However, a text editor application could as easily own multiple bus names (for example, org.kde.KWrite in addition to generic TextEditor), have multiple objects (maybe /org/kde/documents/4352 where the number changes according to the document), and each object could implement multiple interfaces, such as org.freedesktop.DBus.Introspectable, org.freedesktop.BasicTextField, org.kde.RichTextDocument.
D-Bus 消息类型
消息通过 D-Bus 在进程间传递。有四类消息:
- Method call 消息:将触发对象的一个 method
- Method return 消息:触发的方法返回的结果
- Signal 消息:通知,可以看作为事件消息。
- Error 消息:触发的方法返回一个异常
相应工具
Command-line 命令行工具
- dbus-daemon:Message bus daemon
- dbus-launch:从 shell 脚本来启动 message bus 工具
- dbus-send:发送消息到 message bus
- dbus-monitor:debug probe to print message bus messages
- dbus-uuidgen:生成 UUIDs 工具
使用示例:
## launch message bus
$ dbus-launch --sh-syntax
## dbus-send
# send signal
$ dbus-send --type=signal / org.signal.poweroff.test_signal string:"hello"
# send message_call
$ dbus-send --dest=org.freedesktop.ExampleName \
/org/freedesktop/sample/object/name \
org.freedesktop.ExampleInterface.ExampleMethod \
int32:47 string:'hello world' double:65.32 \
array:string:"1st item","next item","last item" \
dict:string:int32:"one",1,"two",2,"three",3 \
variant:int32:-8 \
objpath:/org/freedesktop/sample/object/name
## dbus-uuidgen
# it just prints a new uuid
$ dbus-uuidgen
ebb40ad49f9d4d8f44faa3bc5fffdc27
# prints the machine UUID by default
$ dbus-uuidgen --get
5b86dc18cce752c5404d2f0a5ffd1885
$ dbus-uuidgen --ensure=/usr/local/var/lib/dbus/machine-iddbus-daemon 启动脚本:
#!/bin/bash
## test for an existing bus daemon, just to be safe
if test -z "$DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS"; then
## if not found, launch a new one
eval $(dbus-launch --sh-syntax --exit-with-session)
echo "D-Bus per-session daemon address is: $DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS"
fiGraphical 图形调试工具
libdbus 使用实例:
Method Call 消息例子:
场景:launcher 访问 db_server 获取设备信息,比如:获取 cpu_id。launcher 作为客户端,db_server 做为服务端
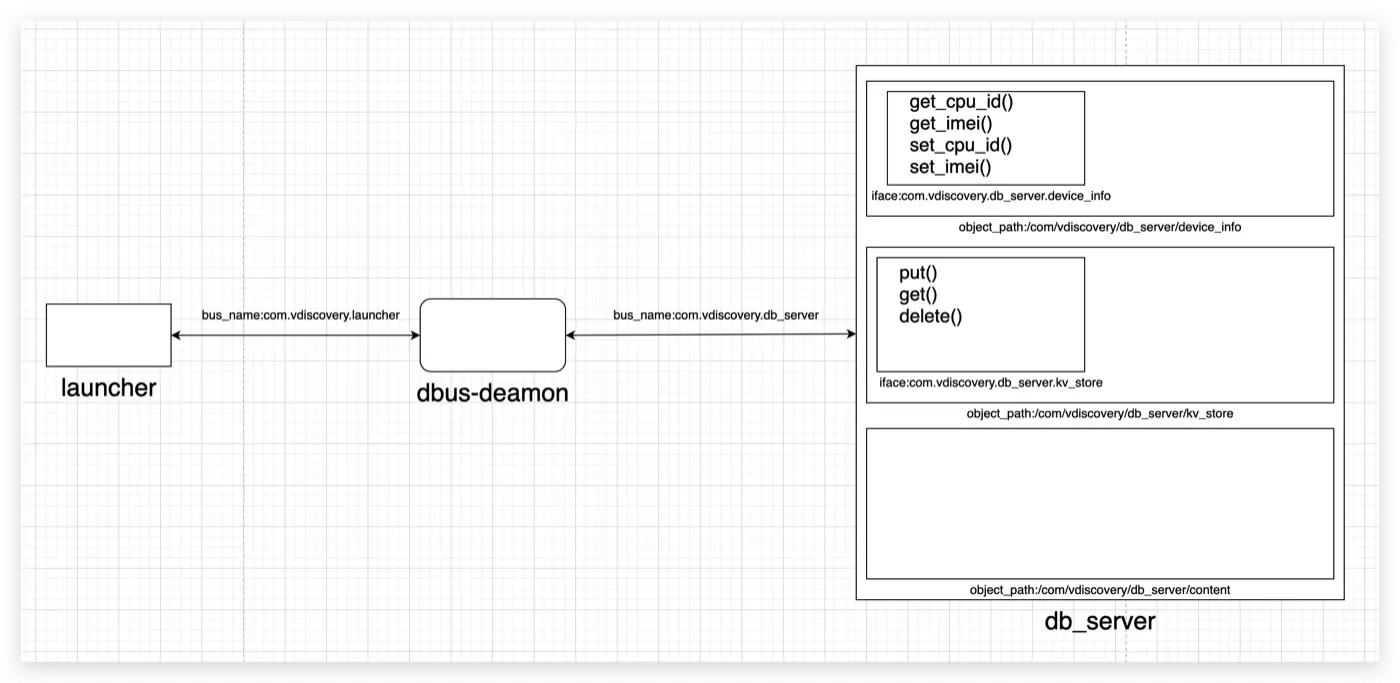
launcher.c 代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "dbus/dbus.h"
#define DBUS_BUS_NAME_LAUNCHER "com.vdiscovery.launcher"
// bus_name
#define DBUS_BUS_NAME_DB_SERVER "com.vdiscovery.db_server"
// object
#define DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO "/com/vdiscovery/db_server/device_info"
// iface
#define DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO "com.vdiscovery.db_server.device_info"
// method
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_GET_IMEI "get_imei"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_GET_CPU_ID "get_cpu_id"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_SET_IMEI "set_imei"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_SET_CPU_ID "set_cpu_id"
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
dbus_bool_t ret = 0;
DBusError err;
DBusConnection* conn = NULL;
dbus_error_init(&err);
// 1.获取链接
conn = dbus_bus_get(DBUS_BUS_SESSION, &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
printf("bus get err : %s\n", err.message);
return -1;
}
// 2.注册自己的name
dbus_bus_request_name(conn, DBUS_BUS_NAME_LAUNCHER, DBUS_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING, &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
printf("bus request name err : %s\n", err.message);
return -1;
}
// 3.创建消息
DBusMessage* req = dbus_message_new_method_call(
DBUS_BUS_NAME_DB_SERVER,
DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO,
DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO,
DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_SET_CPU_ID);
// 3.1.添加携带信息
char* cpu_id = "123456";
dbus_message_append_args(req, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &cpu_id, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
// 4.获取回应消息
DBusMessage* reply = dbus_connection_send_with_reply_and_block(conn, req, 1000 * 4, &err);
char* reply_str = NULL;
dbus_message_get_args(reply, &err, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &reply_str, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
printf("set_cpu_id:%s, reply:reply_str = %s\n", cpu_id, reply_str);
return 0;
}db_server.c 代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "dbus/dbus.h"
// 应用唯一表示:name
#define DBUS_BUS_NAME_DB_SERVER "com.vdiscovery.db_server"
// device_info
#define DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO "/com/vdiscovery/db_server/device_info"
#define DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO "com.vdiscovery.db_server.device_info"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_GET_IMEI "get_imei"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_GET_CPU_ID "get_cpu_id"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_SET_IMEI "set_imei"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_SET_CPU_ID "set_cpu_id"
// kv store
#define DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_KV_STORE "/com/vdiscovery/db_server/kv_store"
#define DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_KV_STORE "com.vdiscovery.db_server.kv_store"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_KV_PUT "put"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_KV_GET "get"
#define DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_KV_DELETE "delete"
// content
#define DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_CONTENT "/com/vdiscovery/db_server/content"
DBusHandlerResult _get_imei(DBusConnection* connection, DBusMessage* message, void* user_data) {
// todo: do something: 从数据库取
DBusMessage* reply = dbus_message_new_method_return(message);
char* imei_str = "imei:fasdfasdflfasdk";
dbus_message_append_args(reply, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &imei_str, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
dbus_connection_send(connection, reply, NULL);
return DBUS_HANDLER_RESULT_HANDLED;
}
DBusHandlerResult _get_cpu_id(DBusConnection* connection, DBusMessage* message, void* user_data) {
// todo: do something: 从数据库取
DBusMessage* reply = dbus_message_new_method_return(message);
char* cpu_id_str = "cpu_id:231412341";
dbus_message_append_args(reply, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &cpu_id_str, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
dbus_connection_send(connection, reply, NULL);
return DBUS_HANDLER_RESULT_HANDLED;
}
DBusHandlerResult _set_imei(DBusConnection* connection, DBusMessage* message, void* user_data) {
DBusError error;
dbus_error_init(&error);
char* req_str = NULL; // json
dbus_message_get_args(message, &error, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &req_str, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
printf("req_str: %s\n", req_str);
// todo: do something with req_str, 存到数据库
DBusMessage* reply = dbus_message_new_method_return(message);
char* succ_str = "store success";
dbus_message_append_args(reply, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &succ_str, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
dbus_connection_send(connection, reply, NULL);
return DBUS_HANDLER_RESULT_HANDLED;
}
DBusHandlerResult _set_cpu_id(DBusConnection* connection, DBusMessage* message, void* user_data) {
DBusError error;
dbus_error_init(&error);
char* req_str = NULL; // json
dbus_message_get_args(message, &error, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &req_str, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
printf("req_str: %s\n", req_str);
// todo: do something with req_str, 存到数据库
DBusMessage* reply = dbus_message_new_method_return(message);
char* succ_str = "store success";
dbus_message_append_args(reply, DBUS_TYPE_STRING, &succ_str, DBUS_TYPE_INVALID);
dbus_connection_send(connection, reply, NULL);
return DBUS_HANDLER_RESULT_HANDLED;
}
DBusHandlerResult device_info_handler(DBusConnection* connection, DBusMessage* message, void* user_data) {
if (dbus_message_is_method_call(message, DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO, DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_GET_IMEI)) {
return _get_imei(connection, message, user_data);
} else if (dbus_message_is_method_call(message, DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO, DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_GET_CPU_ID)) {
return _get_cpu_id(connection, message, user_data);
} else if (dbus_message_is_method_call(message, DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO, DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_SET_IMEI)) {
return _set_imei(connection, message, user_data);
} else if (dbus_message_is_method_call(message, DBUS_IFACE_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO, DBUS_METHOD_CALL_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO_SET_CPU_ID)) {
return _set_cpu_id(connection, message, user_data);
} // ...
return DBUS_HANDLER_RESULT_HANDLED;
}
DBusHandlerResult kv_store_handler(DBusConnection* connection, DBusMessage* message, void* user_data) {
// todo
return DBUS_HANDLER_RESULT_HANDLED;
}
DBusHandlerResult content_handler(DBusConnection* connection, DBusMessage* message, void* user_data) {
// todo
return DBUS_HANDLER_RESULT_HANDLED;
}
DBusObjectPathVTable g_device_info_table = {.message_function = device_info_handler};
DBusObjectPathVTable g_kv_table = {.message_function = kv_store_handler};
DBusObjectPathVTable g_content_table = {.message_function = content_handler};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
dbus_bool_t ret = false;
DBusError err;
DBusConnection* conn = NULL;
dbus_error_init(&err);
// 1.获取链接
conn = dbus_bus_get(DBUS_BUS_SESSION, &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
printf("bus get err : %s\n", err.message);
return -1;
}
// 2.注册自己的name
dbus_bus_request_name(conn, DBUS_BUS_NAME_DB_SERVER, DBUS_NAME_FLAG_REPLACE_EXISTING, &err);
if (dbus_error_is_set(&err)) {
printf("bus request name err : %s\n", err.message);
return -1;
}
// 3.注册自己的Object
ret = dbus_connection_register_object_path(conn, DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_DEVICE_INFO, &g_device_info_table, NULL);
ret = dbus_connection_register_object_path(conn, DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_KV_STORE, &g_kv_table, NULL);
ret = dbus_connection_register_object_path(conn, DBUS_OJBECT_DB_SERVER_CONTENT, &g_content_table, NULL);
if (!ret) {
printf("Failed to register a object path for 'TestObject'\n");
return -1;
}
// 4.read/write/despatch消息
while (true) {
dbus_connection_read_write_dispatch(conn, 0);
}
return 0;
}Signal 消息例子:
todo:
配置文件:
启动其它服务:
其它:
我当时是怎么学习 dbus 的?
核心结构体DBusConnection和DBusMessage
Dbus 是如果连接上 dbus-daemon,调用dbus_bus_get(DBUS_BUS_SESSION, &err);就 get 到了?
换一种方式:如果把参数传给程序
- 参数写死
- main 参数
argv - 特定环境变量(程序自定义)
- 配置文件(配置非常多)